Step Polymerization:
In step polymerization polymer build up proceed through a reaction between functional group of monomers. The reaction takes place in a stepwise manner & the polymer build up is slow.
Polycondensation:
polycondensation is brought about by monomers containing two or more reactive groups such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, amino, etc condensing with each other.
For example,
The reaction between hydroxyl group and a carboxyl group, giving an ester and a water molecule.

In case, mono-hydric alcohol (methanol) and a carboxylic acid (acetic acid), the reaction occurs-

Here, -OH, -COOH are reactive functional group. There are no more reactive functional group left with the product and hence it can't react further.
Again,
If we consider the reaction between ethylene glycol & acetic acid, we see-

In this case, one of the hydroxyl groups in ethylene Glycol (EG) has been consumed by acetic acid but this product is still contains another hydroxyl groups which can react with another molecule of acetic acid.

Now, there is no more reactive functional group and can't react further.
again,
if we consider the reaction between two molecules of adipic acid & two molecules of ethylene glycol (EG), we find that one molecule of EG react with another molecule of adipic acid to form a monoester product.

In this case, the product still contains two reactive groups and each one can react with one more molecule of EG or adipic acid.

The reactant product contains one carboxyl & one hydroxyl group, hence capable of reacting further, the product formed from two molecules of EG & two molecules of adipic acid can be written as-

If there are n molecule of adipic acid and n molecule of ethylene glycol, then overall reaction is-
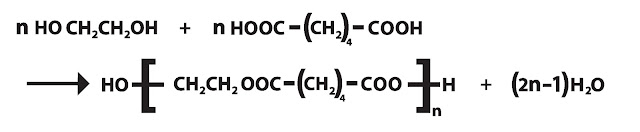
Conclusion of polycondensation:
1/ Monomers should have two reactive functional groups for polymerization to proceed.
2/ Polymerization proceeds by step-wise reaction between reactive functional groups.
3/ Only one type of reaction between two functional groups is involved in polymer formation.
4/ Polymer formed still contains both reactive functional group at its chain ends and hence in active & not dead as in chain polymerization.
